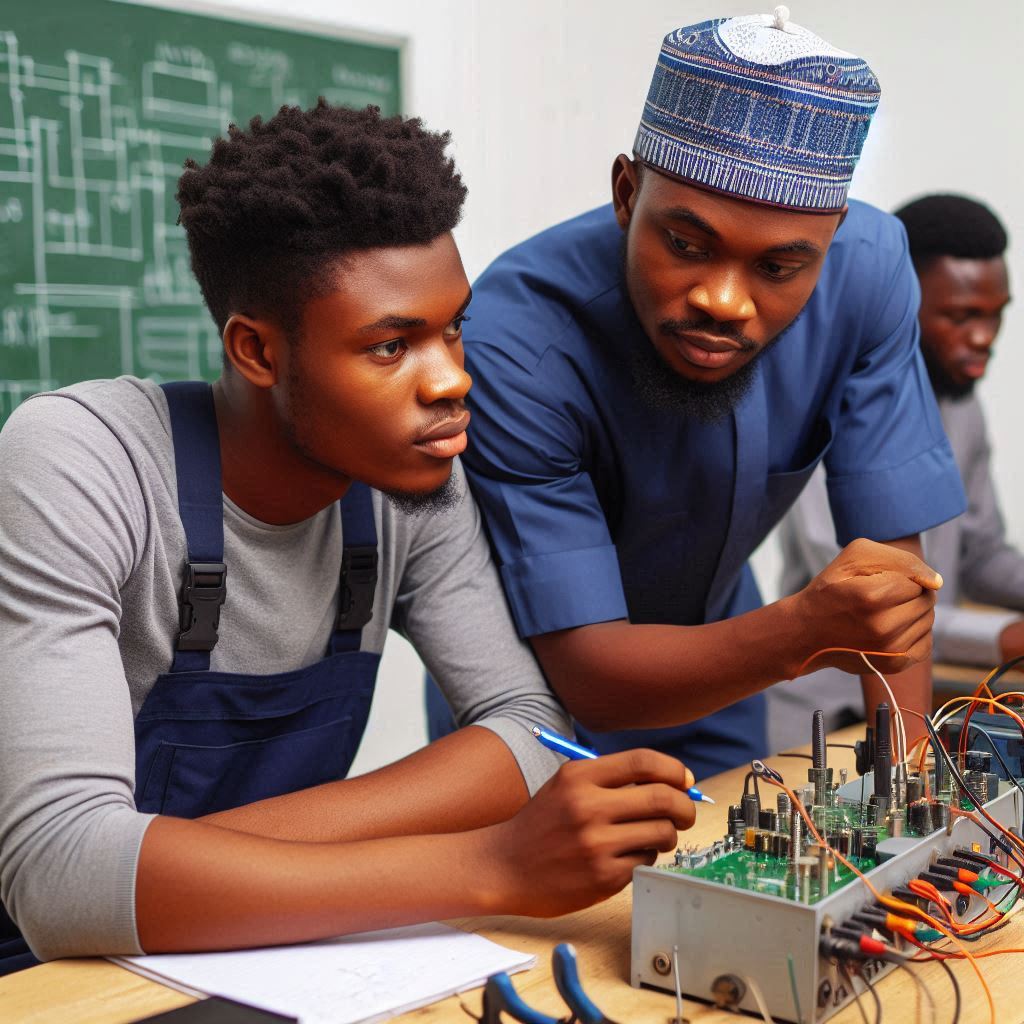
Introduction
Technical education in Nigeria holds immense significance in shaping the nation’s development trajectory. It encompasses skills and knowledge crucial for industrial growth and economic sustainability.
Effective government policies are pivotal in molding the landscape of technical education,
influencing its quality, accessibility, and relevance to national needs.
Importance of Technical Education in Nigeria
Technical education in Nigeria addresses the critical need for skilled manpower across various sectors such as engineering,
technology, and vocational trades.
It bridges the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical application, equipping individuals with hands-on skills essential for employment and entrepreneurship.
This type of education fosters innovation, boosts industrial productivity, and enhances national competitiveness in the global market.
Government policies serve as the backbone of technical education in Nigeria,
guiding its structure, funding, and alignment with national development goals.
Policies determine curriculum standards, accreditation processes, and the establishment of technical institutions across the country.
They also influence partnerships with industries, ensuring that educational programs remain relevant and responsive to evolving market demands.
The Nigerian government has implemented several frameworks to bolster technical education. These include the National Policy on Education, which emphasizes the integration of technical and vocational training into mainstream education.
Additionally, initiatives like the National Board for Technical Education (NBTE) oversee accreditation, curriculum development,
and quality assurance in technical institutions nationwide.
Such frameworks ensure that standards are upheld and that graduates are equipped with skills that meet industry expectations.
Challenges and Areas for Improvement
Despite efforts, challenges persist in the realm of technical education.
Insufficient funding often hampers infrastructure development and faculty training, limiting the capacity of institutions to deliver quality education.
There is also a need for continuous curriculum review to align with technological advancements and industry trends.
Addressing these challenges requires sustained commitment from policymakers,
educators, and stakeholders to create an enabling environment for technical education to thrive.
In general, technical education remains a cornerstone of Nigeria’s development agenda, offering pathways to employment, entrepreneurship, and national prosperity.
Government policies play a crucial role in shaping this educational landscape, ensuring its relevance and effectiveness in meeting societal needs.
By addressing challenges and fostering innovation,
Nigeria can harness the full potential of technical education to drive sustainable growth and economic transformation.
Looking ahead, ongoing collaboration between government, industries, and educational institutions will be essential.
This synergy can enhance curriculum relevance, improve infrastructure, and expand access to technical education across diverse regions of Nigeria.
As global trends and technologies evolve,
adaptive policies will be necessary to equip Nigerian youth with the skills needed to thrive in the 21st-century economy.
Historical perspective of government policies on technical education
In Nigeria, the government has long recognized the importance of technical education in driving economic development and addressing societal needs.
Over the years,
there have been various policies and initiatives aimed at improving the quality and relevance of technical education in the country.
Evolution of government policies
- In the early years of independence, the Nigerian government placed a strong emphasis on technical education as a means to develop a skilled workforce capable of contributing to the country’s industrialization.
- The first major policy initiative in this regard was the establishment of technical colleges across the country to provide vocational training in various trades and crafts.
- Subsequently, the government introduced the National Policy on Education in 1977, which outlined the objectives and strategies for improving technical education in Nigeria.
- The policy emphasized the need for a comprehensive and integrated approach to technical education, with a focus on practical skills development and industry-relevance.
Key reforms and initiatives
- The Technical and Vocational Education Training (TVET) policy was introduced in 2010 to further strengthen technical education in Nigeria by aligning it with international best practices.
- Under this policy, efforts were made to enhance the quality of technical education through curriculum development, teacher training, and infrastructure improvement.
- The government also established the National Board for Technical Education (NBTE) to regulate and accredit technical institutions in the country, ensuring standards are met.
- In recent years, there has been a push towards promoting entrepreneurship and innovation in technical education, with initiatives such as the YouWiN! program targeting youth empowerment through skills development.
- Furthermore, partnerships with industry and international organizations have been forged to enhance the practical relevance of technical education and provide students with exposure to real-world challenges.
- Overall, the evolution of government policies on technical education in Nigeria reflects a commitment to improving the quality and relevance of vocational training to meet the demands of a rapidly changing economy.
- While challenges remain, such as funding constraints and limited access to technical education in rural areas, ongoing efforts are being made to address these issues and ensure that technical education continues to play a vital role in Nigeria’s development.
Read: Scholarships for Counsellor Education Students
Current Challenges Facing Technical Education in Nigeria
Technical education in Nigeria faces significant challenges that hinder its quality and effectiveness.
These issues impact students, teachers, and the economy at large, posing obstacles to the country’s socio-economic development.
Inadequate Funding and Infrastructure
Insufficient financial allocation to technical education cripples infrastructure development.
Without modern facilities and equipment, practical learning suffers, limiting students’ hands-on experience.
This lack of resources also affects the quality of teaching and research, hindering innovation and skill development.
Mismatch Between Curriculum and Industry Needs
The curriculum often fails to align with current industry requirements, leaving graduates unprepared for the job market.
Outdated content and theoretical emphasis without practical application diminish students’ employability and career prospects.
This mismatch exacerbates unemployment and underemployment rates among technical graduates.
Shortage of Qualified Instructors
There is a severe shortage of qualified instructors in technical education. Many skilled professionals opt for more lucrative opportunities in industry rather than academia.
This deficit leads to larger class sizes, reduced individual attention, and lower teaching quality. Consequently, students receive inadequate guidance and mentorship critical for skill acquisition.
Limited collaboration between technical institutions and industries hampers practical training and internship opportunities.
Real-world exposure is crucial for students to bridge the gap between classroom learning and industry demands.
Without industry partnerships, students may graduate without essential practical skills, further perpetuating unemployment.
Quality Assurance and Accreditation Issues
Issues with accreditation and quality assurance undermine the credibility of technical education institutions. Unaccredited programs diminish students’ trust in the education system and limit their access to employment opportunities.
Poor oversight also leads to inconsistencies in educational standards across institutions, affecting overall education quality.
Impact on Students, Teachers, and the Economy
These challenges have profound effects on various stakeholders in the education sector and the broader economy. Students face reduced learning outcomes and limited job prospects due to inadequate skills.
Teachers experience job dissatisfaction and burnout from heavy workloads and lack of resources.
Economically, the country suffers from a shortage of skilled labor necessary for industrial growth and technological advancement.
Industries face challenges in finding qualified personnel, leading to inefficiencies and reduced competitiveness.
This cycle perpetuates underdevelopment and slows down economic progress.
Addressing these challenges requires a multifaceted approach involving increased funding,
curriculum reform, enhanced teacher training, industry collaboration, and stringent quality assurance measures.
By investing in technical education and aligning it with industry needs,
Nigeria can cultivate a skilled workforce capable of driving economic growth and development in the 21st century.
Read: Role of Technology in Business Education in Nigeria
Examination of existing government policies on technical education
Analyzing current policies and programs
The Nigerian government has put in place several policies and programs aimed at promoting technical education in the country.
One of the key policies is the National Policy on Education,
which recognizes the importance of technical and vocational education in national development.
This policy provides a framework for the development of technical education and outlines strategies for improving the quality of instruction and training in technical institutions.
In addition to the National Policy on Education,
the government has also established bodies such as the National Board for Technical Education (NBTE)
and the Technical Vocational Education and Training (TVET) Board to oversee the implementation of technical education programs.
These bodies work to ensure that technical institutions meet the required standards and that students receive quality training that is relevant to the needs of the workforce.
Evaluating strengths and weaknesses
While the government has made concerted efforts to promote technical education,
there are still some challenges that need to be addressed.
One of the strengths of the current policies is the focus on increasing access to technical education for students across the country.
This has led to a significant increase in the number of technical institutions and students enrolling in technical programs.
However, there are also weaknesses in the system,
such as the lack of adequate funding for technical institutions and the outdated curriculum that does not always align with the needs of the workforce.
This has led to a mismatch between the skills that students acquire in technical institutions and what employers actually require in the workplace.
Another weakness is the limited availability of industry-relevant equipment and materials in technical institutions,
which hinders the practical training of students.
This lack of hands-on experience can make it difficult for students to transition successfully from the classroom to the workplace,
thereby reducing their employability.
Recommendations for improvement
Overall, while there have been significant efforts by the Nigerian government to promote technical education,
there is still room for improvement.
To address the weaknesses identified, the government should consider the following recommendations:
- Increasing funding for technical institutions to improve infrastructure and resources
- Updating the curriculum to ensure it is relevant to the needs of the workforce
- Providing more industry partnerships to ensure students have access to practical training opportunities
- Enhancing teacher training programs to improve the quality of instruction in technical institutions
By implementing these recommendations,
the government can strengthen its policies on technical education and better address the needs of students and the workforce in Nigeria.
Read: Counsellor Education Curriculum in Nigerian Schools

Uncover the Details: Agricultural Science Competitions for Nigerian Students
Recommendations for improving government policies on technical education
- Creation of specialized technical education task force: The government should establish a task force specifically dedicated to overseeing and implementing policies related to technical education.
- Investment in infrastructure: It is crucial for the government to allocate sufficient funds towards building and maintaining state-of-the-art facilities in technical institutions.
- Curriculum review: Regularly updating the technical education curriculum to align with industry demands and technological advancements is essential for producing skilled graduates.
- Teacher training and development: Providing continuous training for technical education teachers will ensure they are equipped with the necessary skills and knowledge to deliver high-quality education.
- Industry partnerships: Collaborating with industries to develop internship programs and job placement opportunities for technical education students will bridge the gap between education and employment.
- Enhanced career guidance: Offering comprehensive career guidance services to students will help them make informed decisions about their future and choose the right technical education path.
- Research and innovation: Promoting a culture of research and innovation in technical education institutions will drive the development of cutting-edge technologies and solutions.
- Quality assurance mechanisms: Implementing quality assurance measures to monitor and evaluate the effectiveness of technical education programs will ensure they meet the required standards.
- Advocacy and awareness campaigns: Launching advocacy and awareness campaigns to promote the value and importance of technical education will help change societal perceptions and attitudes towards it.
- Incentives for stakeholders: Providing incentives such as tax breaks or grants to educational institutions and industry stakeholders who actively contribute to promoting technical education will encourage their participation.
Importance of collaboration between the government, educational institutions, and industry stakeholders
Collaboration between the government, educational institutions, and industry stakeholders is essential for the successful implementation of the above recommendations. Here are some reasons why it is crucial:
- Access to resources: Collaboration allows for the pooling of resources, expertise, and knowledge from each sector, maximizing the impact of policies on technical education.
- Relevance to industry needs: Industry stakeholders can provide valuable insights into the skills and competencies required in the workforce, ensuring that technical education programs remain relevant and up-to-date.
- Workforce development: By working together, the government, educational institutions, and industry stakeholders can create a more seamless pathway for students to transition from education to employment, filling the skills gap in the workforce.
- Networking opportunities: Collaboration fosters networking opportunities for students, educators, and industry professionals, allowing for meaningful interactions that can lead to internships, mentorships, and employment opportunities.
- Economic growth: A well-coordinated collaboration between these stakeholders can drive economic growth by producing a skilled workforce that meets the demands of industries and fuels innovation and productivity.
In review, enhancing government policies on technical education
requires a multi-faceted approach that involves not just the government but also educational institutions and industry stakeholders.
By implementing the recommended strategies and fostering collaboration,
Nigeria can ensure that its technical education system produces
highly skilled individuals who contribute to the country’s socio-economic development and global competitiveness.
Read: Career Paths for Graduates of Counsellor Education
Case studies of successful technical education programs in Nigeria
Federal Government’s National Technical Skills Acquisition Programme (NTSAP)
The NTSAP program was launched to equip young Nigerians with relevant technical skills to meet industry demand.
Through partnerships with technical colleges and industry stakeholders,
the program has successfully trained thousands of students in various technical fields such as welding,
carpentry, electrical installation, and automotive repair.
Graduates of the NTSAP program have been able to secure gainful employment in the manufacturing and construction sectors,
contributing to economic growth and reducing unemployment rates in the country.
State Government’s Vocational Training Centers
Several state governments in Nigeria have established vocational training centers to provide technical education and skills training to youth in their respective states.
These centers offer courses in areas such as computer programming, plumbing, tailoring, and agricultural mechanization.
By partnering with local industries and trade associations,
these centers have been able to produce skilled workers who are in high demand in the job market.
Graduates of these programs have gone on to start their businesses or work in established firms,
thereby contributing to the growth of their communities.
Private Sector’s Apprenticeship Programs
Some private companies in Nigeria have implemented apprenticeship programs to train young individuals in technical skills specific to their industry.
These programs are usually hands-on and provide participants with real-world experience while earning a stipend.
Through mentorship and on-the-job training,
apprentices are able to acquire specialized skills that make them valuable assets to their employers.
By investing in such programs,
the private sector not only addresses the skills gap in their industry but also develops a pipeline of skilled workers for future employment opportunities.
Non-Governmental Organizations (NGOs) Support for Technical Education
NGOs in Nigeria have also played a crucial role in supporting technical education initiatives in the country.
By providing scholarships, grants, and mentorship programs, these organizations have been able to empower young individuals with the skills and resources needed to pursue technical careers.
For example, the Tony Elumelu Foundation has a technical skills development program that offers training in fields such as ICT,
agribusiness, and renewable energy.
By partnering with schools and vocational centers,
NGOs can reach a wider audience and make a significant impact on the technical education landscape in Nigeria.
Public-Private Partnerships in Technical Education
Collaboration between the government, private sector,
and academic institutions has proven to be an effective model for advancing technical education in Nigeria.
Through joint initiatives and funding, these partnerships have enabled the development of state-of-the-art training facilities,
curriculum enhancements, and industry-relevant research projects.
By aligning the needs of the industry with the skills of graduates,
these partnerships bridge the gap between education and employment, ensuring a seamless transition for students into the workforce.
Examples of successful public-private partnerships include the Dangote Academy and the Siemens Mechatronics Training Center,
both of which have been instrumental in producing highly skilled technicians and engineers for the Nigerian workforce.
Uncover the Details: Government Policies on Building Technology Education
Find Out More: Government Policies on Vocational Education in Nigeria
Conclusion
In this section, we have explored the crucial role of government policies in shaping technical education in Nigeria.
The discussion highlighted several key points that underscore the importance of proactive governmental intervention in this sector.
By focusing on these points, we can better understand why government support and investment are crucial for the overall development of Nigeria.
Importance of Technical Education
Technical education equips individuals with practical skills that are essential for economic growth and national development.
It bridges the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical application, preparing students for careers in various industries.
Transform Your Career with Expert Guidance
Get personalized mentorship consulting that’s tailored to your unique path. Our expert advice is actionable and exclusive.
Get StartedDespite its importance, technical education in Nigeria faces numerous challenges such as inadequate funding, outdated curriculum, and a shortage of qualified teachers.
These challenges hinder the sector’s ability to meet the demands of a rapidly evolving technological landscape.
Government policies play a pivotal role in addressing these challenges.
Effective policies can allocate sufficient funding to improve infrastructure, update curriculum to align with industry needs, and provide training for teachers to enhance their skills.
Impact of Policy Implementation
When implemented effectively, these policies create an enabling environment for technical education to thrive.
They encourage innovation, entrepreneurship, and industrial growth by producing skilled professionals who can drive technological advancements and economic prosperity.
Looking at international best practices, countries that prioritize technical education often experience accelerated development in sectors such as manufacturing, engineering, and information technology.
Nigeria can emulate these models to foster similar progress.
Therefore, there is a pressing need for the Nigerian government to prioritize technical education.
By investing in modern facilities, updating curricula, and providing adequate training for educators, the government can ensure that students receive quality education that meets global standards.
In closing, the development of technical education in Nigeria hinges significantly on robust government support and investment.
Addressing funding gaps, updating curricula, and enhancing teacher training are critical steps toward creating a skilled workforce capable of driving sustainable development.
It is imperative for policymakers to recognize that technical education is not just an educational issue but a national imperative.
By investing wisely in this sector, Nigeria can unlock its full potential, empower its youth, and position itself as a competitive player in the global economy.
Moving Forward
As we move forward, let us advocate for policies that prioritize technical education.
Together, we can build a prosperous future for Nigeria where every individual has the opportunity to contribute meaningfully to the nation’s growth and development.
Let your voice be heard in supporting initiatives that promote technical education. Encourage policymakers to allocate resources and implement reforms that will shape a brighter tomorrow for generations to come.
In essence, the journey towards a robust technical education system in Nigeria begins with decisive governmental action and sustained public commitment.